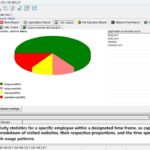
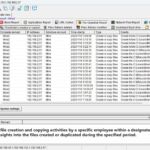
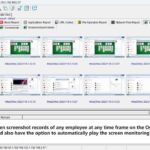
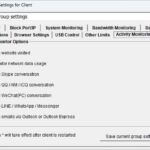
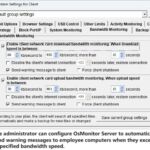
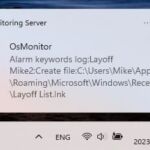
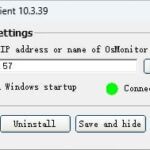
The GPA algorithm (Generalized Processor Sharing) is a scheduling algorithm used for fair bandwidth allocation and resource management in networks. The difficulty of implementing GPA depends on the complexity of the network system and the level of precision required. To implement the GPA algorithm, programming and configuration of network devices are necessary to ensure that the bandwidth is allocated according to certain fairness principles while monitoring and adjusting network traffic in real-time.
The difficulty of implementing the GPA algorithm in a network behavior management system depends on specific application scenarios and system requirements. Generally, the implementation of the GPA algorithm may involve the following steps:
- Data collection: Gathering behavior data from network users, such as browsing history, download activities, communication logs, etc.
- Data preprocessing: Cleaning and organizing the collected raw data, removing redundant information, and extracting relevant features.
- Behavior analysis: Applying the GPA algorithm to analyze and model user behavior data, identifying abnormal behavior or potential threats.
- Risk assessment: Evaluating the risk of user behavior based on the analysis results, determining whether the behavior is trustworthy or suspicious.
- Response measures: Based on the risk assessment results, the system can take appropriate response measures, such as blocking access or issuing alerts.
The difficulty of implementing the GPA algorithm mainly depends on the following factors:
- Data scale: If handling large-scale user behavior data, the implementation of the algorithm may require processing complex data structures and algorithm optimizations.
- Feature extraction: Extracting meaningful features from raw data is a crucial step that may involve the use of machine learning or other techniques to assist with feature extraction.
- Model training and optimization: The effectiveness of the GPA algorithm heavily relies on model training and parameter optimization, which may require substantial data and computational resources.
The GPA algorithm can be applied to various network behavior management scenarios, including but not limited to:
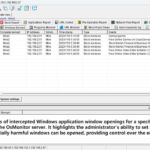
- Network security monitoring: Identifying and preventing potential network attacks by monitoring user network behavior, such as Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS).
- Spam filtering: Identifying and filtering spam emails to reduce user annoyance and network resource waste.
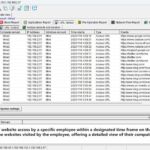
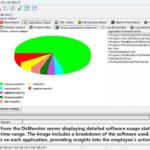
- User behavior analysis: Analyzing and modeling user network behavior to help businesses understand user interests and behavior patterns, enabling personalized services and recommendations.
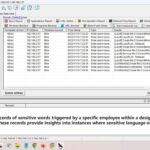
- Internal threat detection: Identifying abnormal behavior or potential internal threats from employees, protecting sensitive data and confidential information within the organization.
In summary, the application of the GPA algorithm in a network behavior management system can provide real-time behavior monitoring and risk assessment, helping to safeguard network security and enhance system trustworthiness. However, the specific application scenarios and implementation difficulties need to be evaluated based on system requirements and data scale.
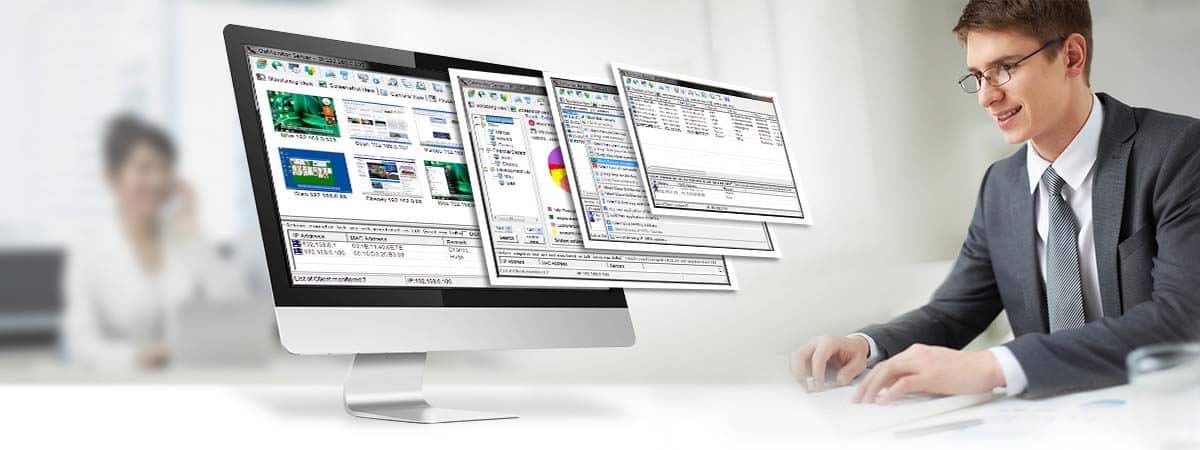
About OsMonitor:
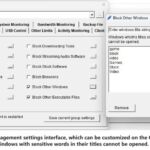
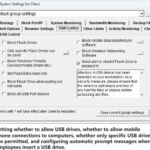
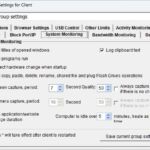
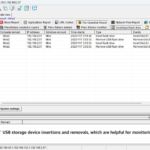
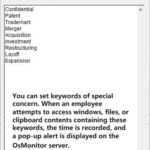
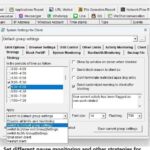
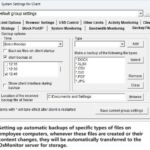
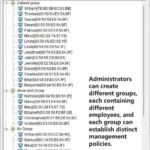
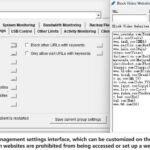
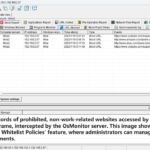
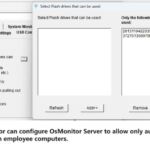
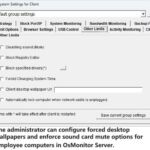
The mission of OsMonitor is to create a Windows computer system tailored for work purposes, effectively regulating employee computer behavior. It enables employers to understand what employees are doing each day, monitoring every action, including screen activity and internet usage. Additionally, it restricts employees from engaging in specific activities such as online shopping, gaming, and the use of USB drives.
OsMonitor, designed purely as software, is remarkably user-friendly and requires no additional hardware modifications. A single management machine can oversee all employee computers. As a leading brand in employee computer monitoring software with over a decade of successful operation, OsMonitor has rapidly captured the global market with its minimal file size and excellent cost-effectiveness compared to similar software. At this moment, thousands of business computers worldwide are running OsMonitor daily.